AI inputs and outputs: An overview¶
You might be looking for...
- If you're looking for information on the different types of
AIMessageobjects, see AI messages.
Introduction¶
The specification of our AI models classes
relies on two classes defined here:
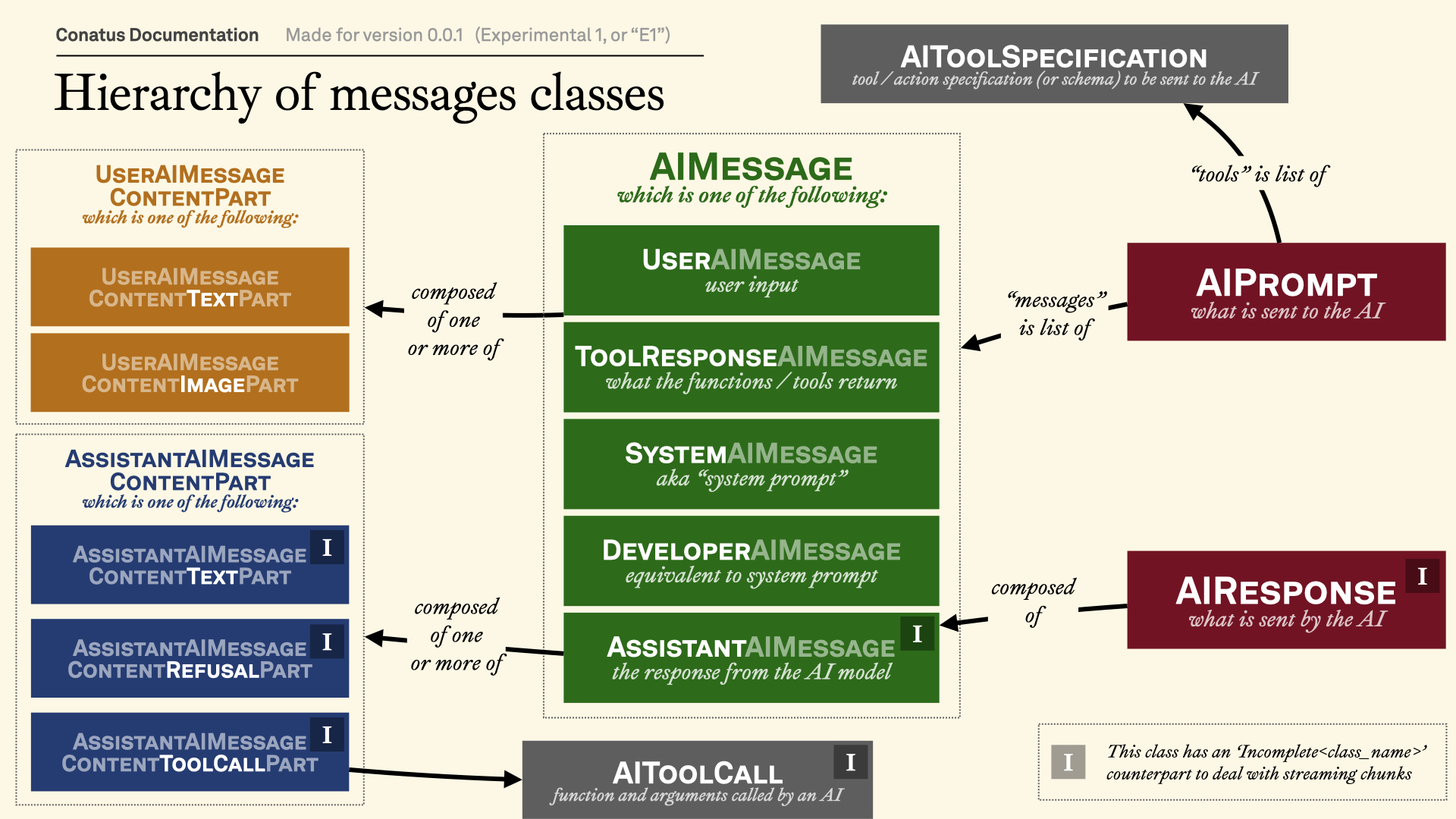
AIPrompt, which is what the user provides to the AI model. The prompt generally consists of:messages, which is a list ofAIMessageobjects. (For more information, see AI messages.)tools, which is a list ofAIToolSpecificationobjects.
AIResponse, which is what the AI model returns to the user.
If you want to customize the AI prompt¶
If you want to create a custom AI prompt, you can use the AIPrompt
constructor as follows:
from conatus import action, AIPrompt
from conatus.models.inputs_outputs.messages import UserAIMessage
@action
def simple_calculator(a: int, b: int) -> int:
return a + b
prompt = AIPrompt(
user="What is the sum of 2222 and 3828?",
system="Use the tools if necessary",
actions=[simple_calculator],
)
If you want to integrate specific AI models¶
New AI models will have to implement mapping functions that convert the
AIPrompt to the specific AI
model's format, and the AIResponse
to the
specific AI model's format.
That work, unfortunately, is somewhat tedious. You can look at the
OpenAIModel implementation for an
example.
One category of classes you might want to rely on are the 'incomplete'
messages. These are messages (mostly counterparts to AssistantAIMessage
and its components)
that are not yet complete, but can be added to each other seamlessly with the
+ operator. (See Incomplete messages for more
information.)
Visual explanation¶
This visualization should help you understand the class hierarchy of the messages:
Main classes¶
AIPrompt(
user: str,
*,
system: str | SystemAIMessage | None = None,
messages: None = None,
previous_messages: None = None,
new_messages: None = None,
tools: Iterable[AIToolSpecification] | None = None,
actions: Iterable[RawAction] | None = None,
computer_use_config: ComputerUseConfig | None = None,
previous_messages_id: None = None,
output_schema: type[OutputSchemaType] | None = None
)
AIPrompt(
user: None = None,
*,
system: str | SystemAIMessage | None = None,
messages: Iterable[ConversationAIMessage],
previous_messages: None = None,
new_messages: None = None,
tools: Iterable[AIToolSpecification] | None = None,
actions: Iterable[RawAction] | None = None,
computer_use_config: ComputerUseConfig | None = None,
previous_messages_id: None = None,
output_schema: type[OutputSchemaType] | None = None
)
AIPrompt(
user: None = None,
*,
system: str | SystemAIMessage | None = None,
messages: None = None,
previous_messages: Iterable[ConversationAIMessage],
new_messages: Iterable[ConversationAIMessage],
tools: Iterable[AIToolSpecification] | None = None,
actions: Iterable[RawAction] | None = None,
computer_use_config: ComputerUseConfig | None = None,
previous_messages_id: str | None = None,
output_schema: type[OutputSchemaType] | None = None
)
AIPrompt(
user: None = None,
*,
system: str | SystemAIMessage | None = None,
messages: None = None,
previous_messages: None = None,
new_messages: Iterable[ConversationAIMessage],
tools: Iterable[AIToolSpecification] | None = None,
actions: Iterable[RawAction] | None = None,
computer_use_config: ComputerUseConfig | None = None,
previous_messages_id: str,
output_schema: type[OutputSchemaType] | None = None
)
AIPrompt(
user: str | None = None,
*,
system: str | SystemAIMessage | None = None,
messages: Iterable[ConversationAIMessage] | None = None,
previous_messages: (
Iterable[ConversationAIMessage] | None
) = None,
new_messages: (
Iterable[ConversationAIMessage] | None
) = None,
tools: Iterable[AIToolSpecification] | None = None,
actions: Iterable[RawAction] | None = None,
computer_use_config: ComputerUseConfig | None = None,
previous_messages_id: str | None = None,
output_schema: type[OutputSchemaType] | None = None
)
Bases: Generic[OutputSchemaType]
Standardized structure for the AI prompt.
Look at the documentation below for more information.
| ATTRIBUTE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
system_message |
The system message for the AI prompt.
TYPE:
|
previous_messages |
The previous messages for the AI prompt. This is optional, and if not provided, the AI prompt will be considered to be in the initial state. Note that it does not include the system message.
TYPE:
|
previous_messages_id |
The ID of the last messages. Some AI providers
like to have this ID in order to link to previous responses. If that
is provided,
TYPE:
|
new_messages |
The new messages for the AI prompt. If
TYPE:
|
tools |
The tools specifications to pass to the AI.
TYPE:
|
computer_use_config |
The configuration for the computer use mode.
TYPE:
|
output_schema |
The (optional) schema of the payload of the AI prompt. If provided, the AI model will be encouraged to return a payload that matches the schema.
TYPE:
|
There are three ways to initialize the AI prompt:
- Simple, new conversation: Pass a string to
user. This will create a new conversation with a single message. - Conversation with multiple messages: Pass a list of messages to
messages. This will create a new conversation with the given messages. - Conversation with history: You can make a distinction between
previous and new messages. This is helpful because some AI providers
(like OpenAI's Response API) allow to send only new messages, as
long as you provide a previous messages ID. In this case, you need
to pass(1) a list of
new_messagesas well as (2) a list ofprevious_messages,previous_messages_id, or both.
In each case, you can optionally pass a system message with system,
a list of tool specifications with tools, a list of actions with
actions, and an output schema with output_schema.
Using tools and actions¶
There are two arguments here:
tools: This is a list of tool specifications, which is a data structure containing the name of the tool and the JSON schema of its specification.actions: This is a list of actions (but it can be anything from anActionStarterPackto normal functions). We handle the processing of converting these actions for you.
The two arguments are not mutually exclusive. If you pass both, the actions will be converted to tools, and added to the list.
actions, unlike tools, need to be JSON serializable
We assume that users that pass actions to AIPrompt
are only passing
actions that are JSON serializable. If you want to pass actions with
variables to references, you need to manually create the
AIToolSpecification
objects and pass them to the tools argument.
Giving an output schema¶
You can also pass an output schema with output_schema.
This communicates to the AI provider that we want the response to follow
that format.
If such an output schema is provided, the BaseAIModel
will create an AIResponse
object with the
output schema type as a generic.
Under the hood, we use a TypeAdapter to
convert the output schema to a Pydantic model. Most JSON-serializable
types (including TypedDicts, BaseModel
s, dataclass, etc.)
should work flawlessly.
There are limitations to what BaseAIModel
classes and AIResponse
deal with output
schemas.
Examples¶
Initialize from a simple string¶
from conatus import AIPrompt
from conatus.models import OpenAIModel
prompt = AIPrompt(
"What did Kurt Gödel say about the US Constitution?"
)
response = OpenAIModel().call(prompt)
Initialize from a list of messages¶
from conatus import AIPrompt
from conatus.models import OpenAIModel
from conatus.models.inputs_outputs.messages import (
SystemAIMessage,
UserAIMessage,
AssistantAIMessage,
)
prompt = AIPrompt(
system=SystemAIMessage(content="You answer very tersely."),
messages=[
UserAIMessage(content="quick, give me a number"),
AssistantAIMessage(content="1234"),
]
)
response = OpenAIModel().call(prompt)
Initialize with a list of actions¶
from conatus import action, AIPrompt
from conatus.models import OpenAIModel
@action
def add_two_numbers(a: int, b: int) -> int:
return a + b
prompt = AIPrompt(
user="what is the sum of 2222 and 3828?",
system="Use the tools if necessary",
actions=[add_two_numbers],
)
response = OpenAIModel().call(prompt)
print(response.tool_calls) # (1)!
# {"name": "add_two_numbers", "arguments": {"a": 2222, "b": 3828}}
- The printing response will actually look a little different in the real world, but you get the idea.
Initialize with an expected output schema¶
from typing import TypedDict
from conatus import AIPrompt
from conatus.models import OpenAIModel
class CoffeeShopMenuItem(TypedDict):
name: str
price: float
prompt = AIPrompt(
user="generate a fake coffee shop menu",
output_schema=list[CoffeeShopMenuItem],
)
response = OpenAIModel().call(prompt)
print(response.structured_output) # (1)!
# > [{"name": "Latte", "price": 3.50}, ...]
Make a distinction between previous and new messages¶
from conatus import AIPrompt
from conatus.models import OpenAIModel, AnthropicAIModel
prompt = AIPrompt(
user="what is the sum of 2222 and 3828?",
system="Use the tools if necessary",
previous_messages=[
UserAIMessage(content="quick, give me a number"),
AssistantAIMessage(content="1234"),
],
new_messages=[
UserAIMessage(content="what is the sum of 2222 and 3828?"),
],
previous_messages_id="rs_1234567890",
)
# In this case, because OpenAI's Response API allows to send only new
# messages, we can use the previous messages ID to link to the previous
# response.
response = OpenAIModel().call(prompt)
# But in the case of Anthropic, we have to send the previous messages
# directly.
response = AnthropicAIModel().call(prompt)
| PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
user
|
The user message. Note that if you also pass a list of
TYPE:
|
system
|
The developer (or system) message. Note that it
will be ignored if
TYPE:
|
messages
|
The messages. Note that it does not include the system
message, which should be passed separately with the
TYPE:
|
previous_messages
|
The previous messages, or conversation history.
TYPE:
|
new_messages
|
The new messages.
TYPE:
|
tools
|
The tool specifications.
TYPE:
|
actions
|
The actions. If you pass both |
computer_use_config
|
The configuration for the computer use mode.
TYPE:
|
previous_messages_id
|
The ID of the last response.
TYPE:
|
output_schema
|
The schema of the payload of the AI prompt.
TYPE:
|
| RAISES | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
ValueError
|
If both a prompt and a list of messages are passed, if neither a prompt nor a list of messages are passed. |
Source code in conatus/models/inputs_outputs/prompt.py
241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 | |
property
¶
requires_stateful_api: bool
Whether the AI prompt requires a stateful API.
This is the case if the AI prompt requires a previous messages ID, but does not require a list of previous messages.
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
bool
|
Whether the AI prompt requires a stateful API. |
property
¶
messages: Iterable[ConversationAIMessage]
The messages of the AI prompt.
Note that it does not include the system message.
property
¶
system_message_as_str: str | None
The text of the system message.
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
str | None
|
The text of the system message. |
property
¶
all_text: str
Get all the text from the AI prompt.
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
str
|
The text from the AI prompt. |
tools_to_markdown() -> str
Get the tools of the AI prompt in markdown format.
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
str
|
The tools of the AI prompt in markdown format. |
Source code in conatus/models/inputs_outputs/prompt.py
output_schema_to_markdown() -> str
Get the output schema of the AI prompt in markdown format.
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
str
|
The output schema of the AI prompt in markdown format. |
Source code in conatus/models/inputs_outputs/prompt.py
to_markdown() -> str
Get the text of the AI prompt.
The expected output is a markdown formatted string, with the following structure:
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
str
|
The text of the AI prompt. |
Source code in conatus/models/inputs_outputs/prompt.py
staticmethod
¶
remove_image_content_parts(
messages: Iterable[ConversationAIMessage],
) -> list[ConversationAIMessage]
Remove the image content parts from the messages.
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
list[ConversationAIMessage]
|
The list of messages without image content parts. |
Source code in conatus/models/inputs_outputs/prompt.py
dataclass
¶
Tool specification to be passed to the AI.
instance-attribute
¶
strict_mode: bool
Whether the tool can be represented through a strict JSON schema mode.
instance-attribute
¶
The JSON schema of the tool, which is a Pydantic model.
property
¶
The JSON schema of the tool.
Alias to the json_schema_pydantic_model
property.
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
type[BaseModel]
|
The JSON schema of the tool. |
Check if the tool specification is equal to another object.
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
bool
|
Whether the tool specification is equal to the other object. |
Source code in conatus/models/inputs_outputs/prompt.py
dataclass
¶
AIResponse(
prompt: AIPrompt[OutputSchemaType],
message_received: AssistantAIMessage,
structured_output: OutputSchemaType | None = None,
finish_reason: FinishReasons | None = None,
usage: CompletionUsage | None = None,
uid: str | None = None,
output_schema_was_converted_to_item_object: bool = False,
)
Bases: Generic[OutputSchemaType]
Base structure for the AI response.
This is the data structure meant for later processing.
Note the new_conversation_history
method, which adds the message_received
to the
messages_sent
field.
instance-attribute
¶
prompt: AIPrompt[OutputSchemaType]
The prompt that was used to create the response.
This is the same as the AIPrompt.prompt
field in the
AIPrompt that was
used to create the response. This is purely a convenience property.
instance-attribute
¶
message_received: AssistantAIMessage
The message received from the AI.
Note that, for now, we only pick one 'choice' from the AI response. Some APIs offer the ability to look at multiple choices, but we do not support that yet.
class-attribute
instance-attribute
¶
structured_output: OutputSchemaType | None = None
The structured output of the AI response, if any.
It can have three possible values:
None: No structured output was found.OutputSchemaType: The structured output was found in the text of the message received.str: No output schema was provided, so we just return the text of the message received.
If you want to get a result without that returns either the structured
output or the text of the message received, you can use the result
property.
class-attribute
instance-attribute
¶
finish_reason: FinishReasons | None = None
The reason the model stopped generating tokens.
class-attribute
instance-attribute
¶
usage: CompletionUsage | None = None
The usage statistics of the AI response.
class-attribute
instance-attribute
¶
uid: str | None = None
The unique identifier of the AI response, as given by the AI provider.
class-attribute
instance-attribute
¶
output_schema_was_converted_to_item_object: bool = False
Whether the output schema was converted to an item object.
property
¶
The messages sent to the AI.
This is the same as the AIPrompt.messages
field in the
AIPrompt that was
used to create the response. This is purely a convenience property.
property
¶
tool_calls: list[AIToolCall | ComputerUseAction]
Get all the tool calls from the assistant message.
This is different from the tool_call_content_parts property,
which is implemented in some of our subclasses, and which returns all
the tool calls in our internal representation. This instead returns
each tool call under the format (tool_name, {arg_name: arg_value}).
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
list[AIToolCall | ComputerUseAction]
|
The tool calls. |
property
¶
tool_call_content_parts_local_execution: list[
AIToolCall | ComputerUseAction
]
Get all the tool calls requiring local execution.
This is different from the tool_call_content_parts property, which
returns all the tool calls in our internal representation. This instead
returns each tool call under the format
(tool_name, {arg_name: arg_value}).
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
list[AIToolCall | ComputerUseAction]
|
The tool calls. |
property
¶
property
¶
conversation_history: list[ConversationAIMessage]
The conversation history, including prompt and message received.
property
¶
all_text: str | None
Get all the text from the assistant message.
Note that this does not include the reasoning.
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
str | None
|
The text from the assistant message. |
property
¶
all_text_including_reasoning: str | None
Get all the text from the assistant message, including the reasoning.
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
str | None
|
The text from the assistant message. |
property
¶
cost: float
Get the cost of the AI response.
Note that if we cannot retrieve the total cost (for whatever reason),
we return -1.
property
¶
result: OutputSchemaType | str
Get the result of the AI response.
Unlike the structured_output
attribute, this property will never return None. If the structured
output is not available, we return the text of the message received.
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
OutputSchemaType | str
|
The result of the AI response. |
Post-initialization hook.
This is where we validate the structured output.
| RAISES | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
ValueError
|
If the structured output is |
Source code in conatus/models/inputs_outputs/response.py
Generate a new conversation history.
Convenience method that adds the message_received
to the messages_sent
field.
If you want to add a ToolResponseAIMessage
after
the message_received
if the AI called a tool, you can set the
add_tool_response_if_tool_call argument to True.
| PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
add_tool_response_if_tool_call
|
If set to
TYPE:
|
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
Iterable[AIMessage]
|
The new conversation history. |
Source code in conatus/models/inputs_outputs/response.py
Get the text of the AI response.
| PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
include_prompt
|
Whether to include the prompt in the output.
TYPE:
|
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
str
|
The text of the AI response. |
Source code in conatus/models/inputs_outputs/response.py
module-attribute
¶
FinishReasons = Literal[
"stop",
"length",
"tool_calls",
"content_filter",
"timeout",
]
Possible reasons for a model to finish generating tokens.
The precise wording varies from provider to provider, so this is meant to be a common interface.