AI messages¶
You might be looking for...
- If you're looking for information on the
AIPromptandAIResponseclasses, see AI inputs and outputs: an overview. - If you're looking for information on content parts, see Content parts.
- If you're looking for information on the tool call data structures, see Tool calls.
- If you're looking for information on data structures for streaming (also known as "incompletes"), see Streaming and Incompletes.
This section describes the main classes for AI messages:
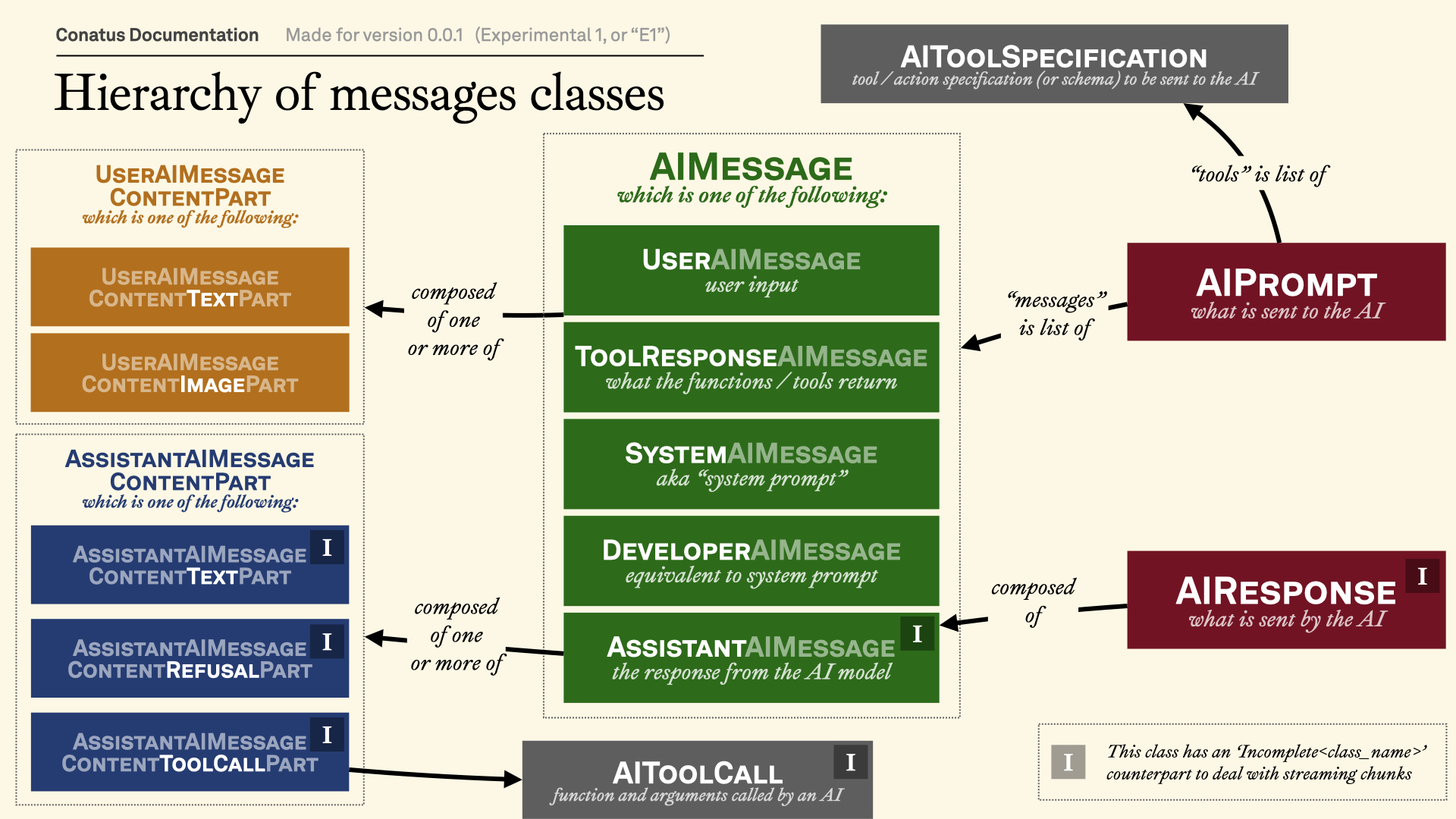
AIMessage, which is aUnionof:UserAIMessage, a message from the user.SystemAIMessage, the system (or developer) promptAssistantAIMessage, a message from the AIToolResponseAIMessage, a message that incorporates a response from a tool call.
Visual explanation¶
This visualization should help you understand the class hierarchy of the messages:
Message categories¶
Note
To make this section more readable, we're not showing the full
path of the classes, but they can also be imported from the
conatus.models.inputs_outputs.messages module.
module-attribute
¶
AIMessage = (
SystemAIMessage
| UserAIMessage
| AssistantAIMessage
| ToolResponseAIMessage
)
Common interface for AI messages.
These are all the messages that can be sent to the AI. A list of these messages
should always be valid as a messages or input field for an AI provider.
Note that not all types of messages will be returned by the AI, but only
AssistantAIMessage.
dataclass
¶
UserAIMessage(
content: str | Iterable[UserAIMessageContentPart],
role: Literal["user"] = "user",
)
User message.
| ATTRIBUTE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
content |
The content of the user message. Can be a string or an
iterable of
TYPE:
|
role |
The role of the user message. Always
TYPE:
|
dataclass
¶
AssistantAIMessage(
content: list[AssistantAIMessageContentPart],
refusal: str | None = None,
role: Literal["assistant"] = "assistant",
)
Assistant message.
This is the message returned by the AI, although it can be passed as an input to show a conversation history.
| ATTRIBUTE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
content |
The content of the assistant message. See
|
refusal |
The refusal of the assistant message.
TYPE:
|
role |
The role of the assistant message. Always
TYPE:
|
property
¶
tool_call_content_parts: list[
AssistantAIMessageContentToolCallPart
]
Get all the tool calls content parts from the assistant message.
property
¶
tool_call_content_parts_local_execution: list[
AssistantAIMessageContentToolCallPart
]
Get all the tool calls requiring local execution.
property
¶
all_text_including_reasoning: str
Get all the text from the assistant message, including reasoning.
classmethod
¶
from_text(text: str) -> Self
Create an assistant message from a text.
Example¶
from conatus.models.inputs_outputs.messages import AssistantAIMessage
msg = AssistantAIMessage.from_text("Sure, will do!")
assert msg.all_text == "Sure, will do!"
| PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
text
|
The text to create the assistant message from.
TYPE:
|
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
Self
|
The assistant message. |
Source code in conatus/models/inputs_outputs/messages.py
dataclass
¶
ToolResponseAIMessage(
content: dict[str, JSONType],
tool_name: str,
tool_call_id: str | None,
success: bool,
role: Literal["tool"] = "tool",
for_computer_use: bool = False,
modified_variables: list[str] | None = None,
)
Tool response message.
This message should not be returned by the AI. It is only used to
indicate that the AI has called a tool. In general, you want to put this
after the AssistantAIMessage
that called the tool.
| ATTRIBUTE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
content |
The content of the tool response message. |
tool_name |
The name of the tool that was called.
TYPE:
|
tool_call_id |
The tool call ID of the tool response message.
TYPE:
|
role |
The role of the tool response message. Always
TYPE:
|
for_computer_use |
Whether the tool response is for computer use. Some providers demand a different format for computer use mode.
TYPE:
|
modified_variables |
The variables that were modified by the tool, if any. |
success |
Whether the tool call was successful. Anthropic requires
this to be
TYPE:
|
property
¶
content_as_string: str
Get the content of the tool response message as a string.
to_markdown() -> str
Get the text of the tool response message.
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
str
|
The text of the tool response message. |
Source code in conatus/models/inputs_outputs/messages.py
dataclass
¶
System message / prompt.
Note that some AI providers call this a "developer message". AI provider classes will need to operate the distinction between system messages and developer messages.
| ATTRIBUTE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
content |
The content of the system message.
TYPE:
|
role |
The role of the system message. Always
TYPE:
|
module-attribute
¶
ConversationAIMessage = (
UserAIMessage
| AssistantAIMessage
| ToolResponseAIMessage
)
Common interface for conversation messages.
These are all the messages that can be part of a conversation. In other
words, everything but the SystemAIMessage
.
Completion usage¶
dataclass
¶
CompletionUsage(
model_name: str | None = None,
prompt_tokens: int = 0,
completion_tokens: int = 0,
total_tokens: int = 0,
cached_used_tokens: int | None = None,
cached_created_tokens: int | None = None,
extra_fields: dict[str, int | None] | None = None,
usage_was_never_given: bool = True,
always_override_previous_usage: bool = False,
)
Bases: Addable
Completion usage statistics.
Note that you can add CompletionUsage
instances together,
which is useful for accumulating usage during streaming.
class-attribute
instance-attribute
¶
model_name: str | None = None
The name of the model used.
class-attribute
instance-attribute
¶
prompt_tokens: int = 0
The number of tokens in the prompt.
class-attribute
instance-attribute
¶
completion_tokens: int = 0
The number of tokens in the completion.
class-attribute
instance-attribute
¶
cached_used_tokens: int | None = None
The tokens that were resulting from a cache read.
class-attribute
instance-attribute
¶
cached_created_tokens: int | None = None
The tokens that were resulted in a cache write.
class-attribute
instance-attribute
¶
Extra fields to store additional usage statistics.
These fields need to be addable as well, and we assume that
the default value is 0.
class-attribute
instance-attribute
¶
usage_was_never_given: bool = True
Flag to indicate that the usage was never given.
This is useful to indicate errors if the usage was not sent back by the AI provider.
class-attribute
instance-attribute
¶
always_override_previous_usage: bool = False
Flag to indicate that the previous usage should be overridden.
In this case, addition will really mean that the previous usage is forgotten and the new usage is used instead.
Add a CompletionUsage and a CompletionUsage.
Note that neither self nor other are modified.
| PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
other
|
The instance of
TYPE:
|
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
CompletionUsage
|
The instance of |
Source code in conatus/models/inputs_outputs/usage.py
__hash__() -> int
Hash a completion usage.
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
int
|
The hash of the completion usage. |
Source code in conatus/models/inputs_outputs/usage.py
Add an incomplete tool call to an incomplete tool call.
| PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
other
|
The other incomplete tool call.
TYPE:
|
| RETURNS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
Self
|
The sum of the two incomplete tool calls. |